Introduction
Forex trading has become increasingly popular in recent years, with more and more individuals looking to capitalize on the fluctuations in currency exchange rates. However, before diving into the world of Forex, it’s essential to understand the basics. In this article, we will cover the fundamental concepts of Forex trading, including currency pairs, exchange rates, bid/ask prices, pips, leverage, margin, trading sessions, order types, technical analysis, fundamental analysis, risk management, and trading strategies.
Currency Pairs
Forex trading involves trading currency pairs, such as EUR/USD, USD/JPY, or GBP/USD. Each currency pair has a base currency and a quote currency. The base currency is the currency being bought or sold, while the quote currency is the currency being used to quote the price.
Exchange Rates
The exchange rate is the price of one currency in terms of another. Exchange rates fluctuate constantly due to supply and demand forces in the market.
Bid/Ask Prices
The bid price is the price at which you can sell a currency, while the ask price is the price at which you can buy. The difference between the bid and ask prices is called the spread.
Pips
A pip is the smallest unit of price movement in Forex, typically 0.0001 of the base currency.
Leverage
Forex trading allows for leverage, which means you can control a large position with a small amount of capital. Leverage can amplify profits, but also increases losses.
Margin
The margin is the amount of capital required to open a trade. Margin requirements vary depending on the broker and the currency pair being traded.
Trading Sessions
Forex markets are open 24/5, with different trading sessions (Sydney, Tokyo, London, New York). Each session has its unique characteristics and market dynamics.
Order Types
There are various order types, including market orders, limit orders, stop-loss orders, and take-profit orders. Each order type serves a specific purpose and can be used to execute trades or manage risk.
Technical Analysis
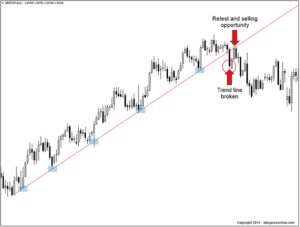
Technical analysis involves studying charts and patterns to predict future price movements. Technical analysts use various tools and indicators to identify trends and potential trading opportunities.
Fundamental Analysis
Fundamental analysis involves studying economic indicators and news to predict future price movements. Fundamental analysts examine factors such as GDP, inflation, and interest rates to forecast currency fluctuations.

Risk Management
Risk management involves managing your capital and minimizing losses. Risk management techniques include position sizing, stop-loss orders, and diversification.
Trading Strategies
There are various trading strategies, including day trading, swing trading, scalping, and position trading. Each strategy has its unique characteristics and requires a different approach to trading.
Conclusion
Forex trading can be a lucrative venture, but it’s essential to understand the basics before getting started. By mastering the concepts outlined in this article, you’ll be well on your way to becoming a successful Forex trader.